Last updated on January 5, 2024
Key Takeaways:
- Gliomas are a type of brain and spinal cord tumor that originate from glial cells.
- Gliomas can be categorized into three main types: astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas.
- Glioma tumors can vary in aggressiveness, with grade IV glioblastoma multiforme being the most malignant.
- Glioma symptoms include headaches, seizures, cognitive difficulties, personality changes, and coordination issues.
- Treatment options for glioma tumors include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy.
- Support mechanisms and lifestyle strategies can improve well-being and quality of life for glioma patients.
- Precision medicine and immunotherapy have revolutionized glioma treatment.
- Stem cell research and gene therapy show promise for advancing glioma treatment.
- Ongoing research aims to identify novel therapeutic targets and improve treatment outcomes for glioma tumors.
The Basics of Glioma Tumors
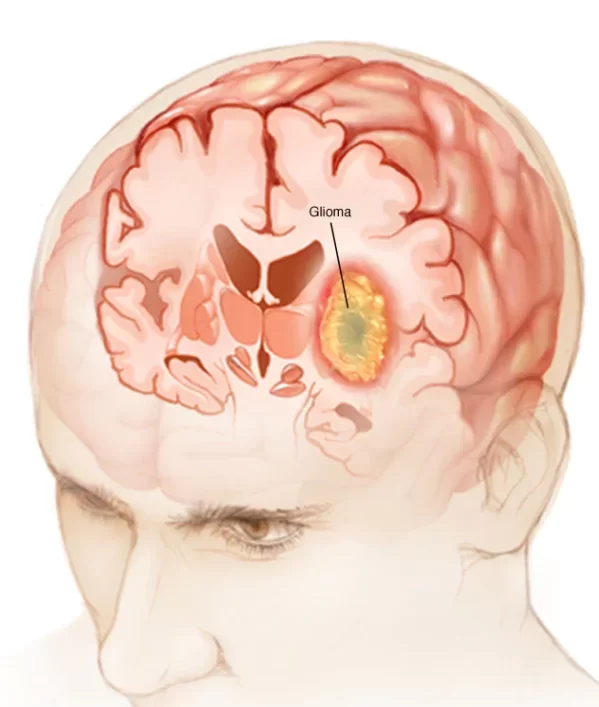
When it comes to understanding glioma tumors, it is crucial to delve into the basics. Gliomas are a type of tumor that originates in the brain and spinal cord. These tumors develop from the glial cells, which are responsible for supporting and nourishing nerve cells.
What are Glioma Tumors and How Do They Form?
Glioma tumors are a result of abnormal growth in the glial cells, which make up the supportive tissue of the brain and spinal cord. These tumors can occur in any part of the central nervous system and can be categorized into three main types: astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas.
Astrocytomas are the most common type of glioma and originate from the star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes. Oligodendrogliomas develop from the cells that produce myelin, the coating around nerve cells. Ependymomas are gliomas that form from the ependymal cells lining the ventricles of the brain.
Although the exact cause of glioma tumors is not yet fully understood, there are certain risk factors associated with their development. These risk factors include exposure to radiation, certain genetic conditions like neurofibromatosis, and a family history of gliomas.
The Different Types of Glioma Tumors
As mentioned earlier, glioma tumors can be classified into three main types based on their origin: astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas. However, within these categories, there are different grades that indicate the aggressiveness of the tumor.
Gliomas are graded on a scale of I to IV, with grade IV being the most aggressive. Grade I tumors are considered the least aggressive, while grade IV tumors, also known as glioblastoma multiforme, are highly malignant and grow rapidly.
In addition to the grades, gliomas can also be classified based on their location within the brain. Some common types include brainstem gliomas, optic nerve gliomas, and cerebral hemisphere gliomas.
Understanding the Symptoms and Diagnosis of Glioma Tumors
Glioma tumors can present a wide range of symptoms depending on their size, location, and grade. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, cognitive difficulties, changes in personality, and problems with balance or coordination.
Diagnosing glioma tumors involves a combination of imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan, and a biopsy to confirm the presence of tumor cells. After the diagnosis, the tumor is usually graded to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Glioma Tumors
When it comes to treating glioma tumors, a multidisciplinary approach is often necessary. The treatment options for gliomas include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy.
Surgery: A Promising Path to Eliminate Glioma
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for glioma tumors. The aim of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to critical brain functions. In some cases, complete removal may not be possible, but the surgeon will strive to alleviate symptoms and reduce the tumor burden.
In recent years, advancements in surgical techniques, such as awake brain surgery and intraoperative MRI, have improved the outcomes for patients undergoing glioma surgery. These techniques allow surgeons to navigate sensitive areas of the brain more precisely, resulting in better tumor resection.
Radiation Therapy: Zapping Glioma Tumors for Good
Radiation therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of glioma tumors. It involves using high-energy X-rays or protons to destroy tumor cells and prevent their growth. Radiation therapy can be administered externally, known as external beam radiation therapy, or internally, using brachytherapy.
For gliomas, external beam radiation therapy is the most common approach. It typically involves daily treatments over several weeks. In some cases, radiation therapy may be employed before or after surgery to target any remaining tumor cells and improve overall outcomes.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Drug Therapy: Fighting Glioma on a Molecular Level
Chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with surgery and radiation therapy to treat glioma tumors. It involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth. Chemotherapy drugs can be given orally or intravenously and may be used in combination to increase effectiveness.
Additionally, targeted drug therapy has emerged as a promising treatment option for gliomas. These drugs specifically target the molecular abnormalities present in glioma cells, enhancing treatment efficacy while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
Coping with Glioma Tumors: Support and Lifestyle Strategies
Dealing with a glioma diagnosis can be challenging not only for the patients but also for their loved ones. Alongside medical treatment, adopting various support mechanisms and lifestyle strategies can significantly improve the overall well-being and quality of life.
Emotional Support: Nurturing Your Mental Well-being
Receiving a glioma diagnosis can bring about a range of emotions, including fear, anxiety, and sadness. It is essential to address these emotions and seek emotional support from professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, who specialize in helping individuals coping with cancer.
Support groups can also be valuable as they provide a safe space to connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, thoughts, and emotions can foster a sense of community and provide additional insights into coping strategies.
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes: Empowering Your Body’s Natural Defense
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and making dietary changes can play a significant role in supporting the body’s natural defense mechanisms against glioma tumors. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides the necessary nutrients to optimize the immune system and maintain overall health.
Engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and getting sufficient sleep are also crucial components of a healthy lifestyle. These practices contribute to improved well-being and can enhance the body’s ability to fight off cancer cells.
Alternative Therapies and Complementary Medicine: Unlocking New Possibilities
Alternative therapies and complementary medicine can offer additional support in managing glioma tumors. Acupuncture, massage therapy, meditation, and yoga are some examples of alternative therapies that have been found to reduce stress, alleviate side effects of treatment, and promote relaxation.
It is important to note that alternative therapies should always be discussed with healthcare professionals to ensure they do not interfere with conventional treatment or compromise its effectiveness.
Latest Research and Future Outlook for Glioma Tumors
Glioma research continues to expand our knowledge and improve treatment options. Numerous advancements have been made in recent years, offering hope for a brighter future for patients.
Advancements in Glioma Treatment: From Precision Medicine to Immunotherapy
Precision medicine, which involves tailoring treatment plans based on the genetic characteristics of the tumor, has revolutionized cancer treatment, including gliomas. By analyzing the genetic makeup of glioma tumors, doctors can identify specific genetic mutations and select targeted therapies that offer the greatest chance of success.
Immunotherapy is another promising approach that aims to harness the body’s immune system to fight cancer. This treatment modality stimulates an immune response against glioma cells, potentially improving outcomes and reducing side effects compared to traditional therapies.
Exploring Cutting-Edge Research: Stem Cells and Gene Therapy
Stem cell research and gene therapy are emerging fields with the potential to transform the treatment landscape for glioma tumors. Stem cells can be used to deliver targeted therapies directly to the tumor site, while gene therapy aims to replace or repair faulty genes that contribute to tumor growth.
These innovative approaches are still in the experimental stage but offer a glimmer of hope for patients who have exhausted traditional treatment options.
Hope on the Horizon: Promising Breakthroughs in Glioma Research
Multiple ongoing research studies are focused on identifying novel therapeutic targets and developing innovative treatments for glioma tumors. Researchers are exploring the role of immunotherapies, targeted therapies, and combination treatments to improve outcomes and extend survival rates.
Additionally, advancements in imaging techniques, such as functional MRI and PET scans, are enhancing the early detection and diagnosis of glioma tumors, leading to better treatment outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding glioma tumors involves delving into the basics, exploring different types and grades, recognizing the symptoms, and diagnosing the condition accurately. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. Coping with glioma tumors involves seeking emotional support, making dietary and lifestyle changes, and considering alternative therapies. Exciting advancements in research offer hope for the future, with precision medicine, immunotherapy, stem cell research, and gene therapy leading the way.
FAQ
Question: What causes glioma tumors to form? – Glioma tumors are a result of abnormal growth in the glial cells, which make up the supportive tissue of the brain and spinal cord. The exact cause of glioma tumors is not yet fully understood, but certain risk factors, such as exposure to radiation, certain genetic conditions, and a family history of gliomas, have been identified.
Question: What are the different types of glioma tumors? – Glioma tumors can be categorized into three main types based on their origin: astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas. Astrocytomas originate from astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas develop from cells that produce myelin, and ependymomas form from ependymal cells lining the brain’s ventricles.
Question: What are the symptoms of glioma tumors? – Glioma tumors can cause a range of symptoms, including headaches, seizures, cognitive difficulties, changes in personality, and problems with balance or coordination. The specific symptoms can vary depending on the size, location, and grade of the tumor.
Question: How are glioma tumors diagnosed? – Diagnosing glioma tumors typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan, and a biopsy to confirm the presence of tumor cells. Once diagnosed, the tumor is usually graded to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Question: What are the treatment options for glioma tumors? – Treatment options for glioma tumors include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. Surgery aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible, while radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or protons to destroy tumor cells. Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill or slow down cancer cells, and targeted drug therapy specifically targets molecular abnormalities in glioma cells.
Question: How can glioma patients cope with the diagnosis? – Coping with a glioma diagnosis involves adopting various support mechanisms and lifestyle strategies. Seeking emotional support from professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, and joining support groups can help address the emotional challenges. Making dietary and lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and getting sufficient sleep, can also improve overall well-being.
Question: Are there any alternative therapies for managing glioma tumors? – Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, meditation, and yoga, can provide additional support in managing glioma tumors. However, it is important to discuss these therapies with healthcare professionals to ensure they do not interfere with conventional treatment or compromise its effectiveness.
Question: What are some promising advancements in glioma research? – Advancements in glioma research include precision medicine, which tailors treatment plans based on the genetic characteristics of the tumor, and immunotherapy, which stimulates an immune response against glioma cells. Stem cell research and gene therapy are also promising fields that show potential in transforming the treatment landscape for glioma tumors. Ongoing research aims to identify novel therapeutic targets and develop innovative treatments for gliomas.
















Be First to Comment